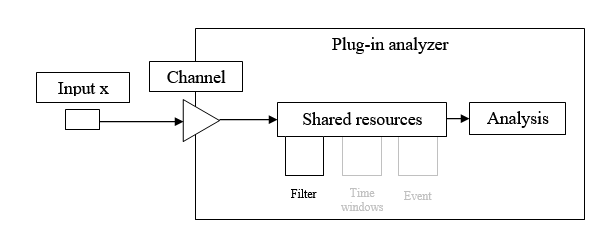
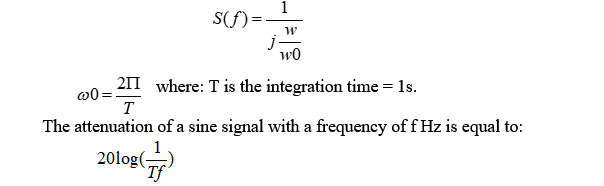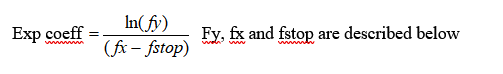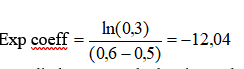NVGate Filter Builder
Filter builder
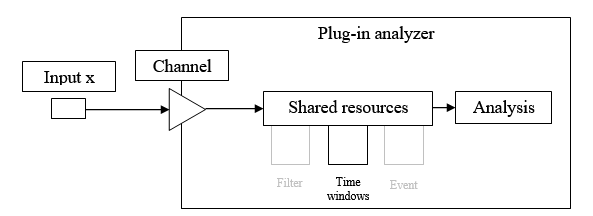
Used to define several filters that can be applied to FFT or Sync. order plug-in input filters.
High-Low pass
Used to design a high-pass filter or a low-pass filter (Butterworth, elliptic…).
- Label: the name of the filter (by default High-Low pass n, with 1 <= n <= 4).
- Type: the type (Low pass or High pass) of the filter.
- Filter order: filter order from 1 to 6. The higher is the order, the steepest is the cut-off slope.
- Applied to: Indicates on witch plug-in the filter can be used. Indeed the construction of the filter requires applying it on signal with the same bandwidth. The determination of the associated plug-in/bandwidth is automatic. De-activated the filter to reset ot.
The other modules (front-end, monitor, resources) operates at the front end input sampling (in connected mode on-line) or to the max player bandwidth (in post analysis mode).
| Apply to | Description |
| Front-end (20 kHz) | To be used on any resources and monitor |
| FFTx (10 kHz) | To be used on the FFT x analyzer only |
Note even if plug-ins run in the same bandwidth, it no possible to share filters between different plug-in.
- Cut-off frequency: the filter cut-off frequency. Its maximum value is the input frequency range. Its minimum value is: FR / 40 (for a Low pass filter) and FR / 400 (for a High pass filter), where FR is the input frequency range.
Warning for measurements including signal phase (i.e: balancing or Bode plot) the cut-off frequency must be chose far (10 times) from the frequency of interest. If not the phase of the low pas filter will affect the phase of the result.
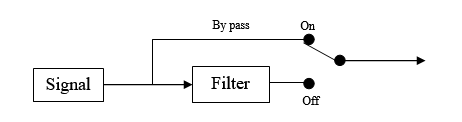
- By-pass: On / Off. The filter is not applied if By-pass is On.
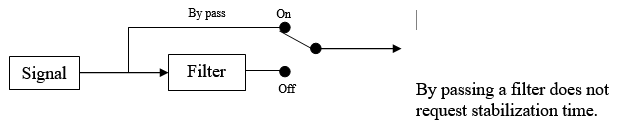
By passing a filter does not request stabilization time.
Pass-Stop band
Used to design a band-pass filter or a band-stop filter.
- Label: the name of the filter (by default Pass-Stop band n, with 1 <= n <= 4).
- Type: the type (Band pass or Band stop) of filter.
- Filter order: 2, 4, 6, 8 or 10. The higher is the order, the steepest is the cut-off.
- Applied to: Indicates on witch plug-in the filter can be used. Indeed the construction of the filter requires applying it on signal with the same bandwidth. The determination of the associated plug-in/bandwidth is automatic. De-activated the filter to reset ot.
The other modules (front-end, monitor, resources) operates at the front end input sampling (in connected mode on-line) or to the max player bandwidth (in post analysis mode).
| Apply to | Description |
| Front-end (20 kHz) | To be used on any resources and monitor |
| FFTx (10 kHz) | To be used on the FFT x analyzer only |
Note: even if plug-ins run in the same bandwidth, it no possible to share filters between different plug-in.
- Low cut-off frequency: the low filter cut-off frequency. Its minimum value is 0.055 * FR, where FR is the input frequency range. However, the following conditions must also be fulfilled:
0.0075 * FR <= B <= 0.5 FR
where B is the bandwidth between Low and high cut-off frequency
and FR is the input frequency range.
- High cut-off frequency: the filter high cut-off frequency. Its maximum value is the input frequency range. However, the following conditions must also be fulfilled: see Low cut-off frequency.
- By-pass: On / Off. The filter is not applied if By-pass is On.
Integrator
Used to design a time integrator filter associated with a high pass filter (to limit gain near DC components).
- Label: the name of the filter (by default Integrator n, with 1 <= n <= ).
- Type: the type (High Pass + single integ. / High Pass + double integ.) of the filter.
- Applied to: Indicates on witch plug-in the filter can be used. Indeed the construction of the filter requires applying it on signal with the same bandwidth. The determination of the associated plug-in/bandwidth is automatic. De-activated the filter to reset ot.
The other modules (front-end, monitor, resources) operates at the front end input sampling (in connected mode on-line) or to the max player bandwidth (in post analysis mode).
| Apply to | Description |
| Front-end (20 kHz) | To be used on any resources and monitor |
| FFTx (10 kHz) | To be used on the FFT x analyzer only |
Note even if plug-ins run in the same bandwidth, it no possible to share filters between different plug-in.
- HP cut-off frequency: the cut-off frequency of the High pass filter contained in this integrator filter. Its maximum value is FR / 2000, and its minimum value is FR / 10000, where FR is the input frequency range.
Warning for measurements including signal phase (i.e: balancing or Bode plot) the cut-off frequency must be chose far (10 times) from the frequency of interest. If not the phase of the low pas filter will affect the phase of the result.
'Integration 'time: the time constant of the integrator filter is equal to 1s. This is fixed value, not a setting.
The frequency response of a first order integrator filter is equal to:
- By-pass: On / Off. The filter is not applied if By-pass is On.
Differentiator
Used to setup a time differentiator filter associated with an exponential average to avoid that small fluctuations of the input signal become important distortions in the output signal.
- Label: the name of the filter (by default Differentiator n, with 1 <= n <= 3).
- Applied to: Indicates on witch plug-in the filter can be used. Indeed the construction of the filter requires applying it on signal with the same bandwidth. The determination of the associated plug-in/bandwidth is automatic. De-activated the filter to reset ot.
The other modules (front-end, monitor, resources) operates at the front end input sampling (in connected mode on-line) or to the max player bandwidth (in post analysis mode).
| Apply to | Description |
| Front-end (20 kHz) | To be used on any resources and monitor |
| FFTx (10 kHz) | To be used on the FFT x analyzer only |
Note even if plug-ins run in the same bandwidth, it no possible to share filters between different plug-in.
- Avg. duration:Filter average duration. By default, the average duration is equal to 0s. This value can be modified by the user. This setting is used to specify the exponential average duration of the differentiator filter
Xmean(n) = λX(n) + (1 – λ)Xmean(n-1) with Xmean(n) the averaged input signal at instant n, X(n) the input signal at instant n and λ the averaging factor.
The following formula is applied to the averaged signal:
Y(n) = (Xmean(n) -Xmean(n-1)) / fs. with, Y(n) the differentiated signal at instant n, Xmean(n) the averaged input signal at instant n and fs the sampling frequency.
- By-pass: On / Off. The filter is not applied if By-pass is On.
Time windows
Used to define time weighting windows that can be applied to FFT blocks.
Force
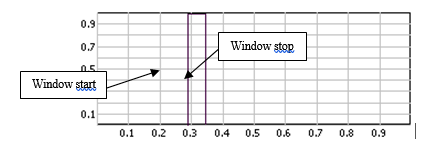
This setting is generally used to set up a uniform time window around the interesting part of the signal such as hammer impact, for example.
- Window Start: Starting point of the window as a percentage of the triggered block size of the plug-in using the window. The block size is the plug-in resolution setting value multiplied by 2.56. ex: for 401 lines resolution the triggered block size is 401*2.56 = 1024 samples.
- Window Stop: Stopping point of the window in percentage of the triggered block size of the plug-in using the window. The block size is the plug-in resolution setting value multiplied by 2.56. ex: for 401 lines resolution the triggered block size is 401*2.56 = 1024 samples.
Note: it is possible to adjust the start and stop values graphically by using drag and drop on the graph.
Response
This setting is generally used to set up a uniform time window around the interesting part of the signal such as the response of an accelerometer after a hammer impact, for example.
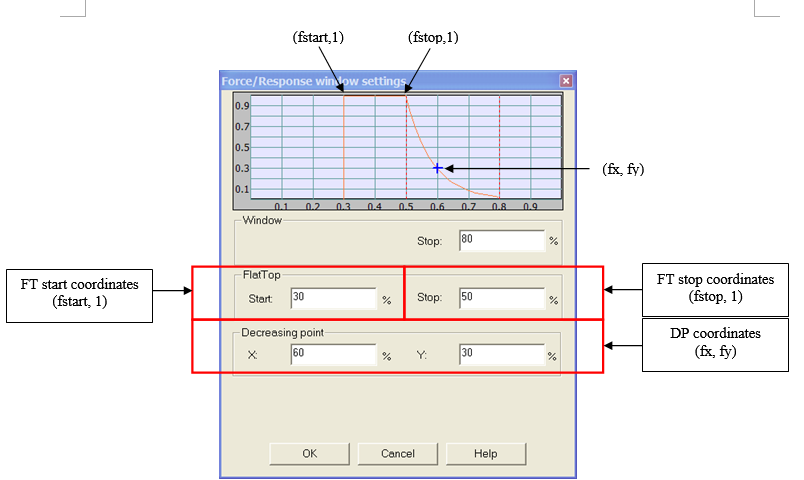
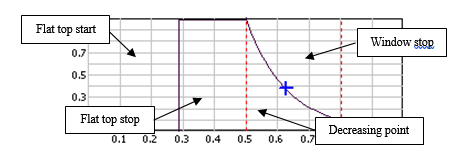
- Window Stop: Stopping point of the window as a percentage of the triggered block size of the plug-in using the window. The block size is the plug-in resolution setting value multiplied by 2.56. ex: for 401 lines resolution the triggered block size is 401*2.56 = 1024 samples.
- Flat top Start: Starting point of the window flat top as percentage of the triggered block size of the plug-in using the window. The block size is the plug-in resolution setting value multiplied by 2.56. ex: for 401 lines resolution the triggered block size is 401*2.56 = 1024 samples.
- Flat top Stop: Stopping point of the window flat top as a percentage of the triggered block size of the plug-in using the window. The block size is the plug-in resolution setting value multiplied by 2.56. ex: for 401 lines resolution the triggered block size is 401*2.56 = 1024 samples.
- Decreasing point X: Abscissa of the intermediate point that determines the decreasing coefficient of the exponential function as a percentage of the triggered block size of the plug-in using the window. The block size is the plug-in resolution setting value multiplied by 2.56. ex: for 401 lines resolution the triggered block size is 401*2.56 = 1024 samples.
- Decreasing 'point Y': Ordinate of the intermediate point that determines the decreasing coefficient of the exponential function as a percentage of the value of the signal.
- Exponential coefficient: this coefficient is calculated with the coordinates of Decreasing point Y and Decreasing point X.
In this example, it then gives
Note: a time window can be applied to several plug-in analyzer channels. The modification of the time window values will be applied to all the channels the time window is active.
Note: it is possible to adjust the values graphically by using drag and drop on the graph.