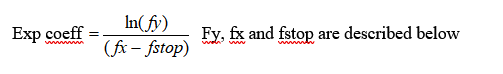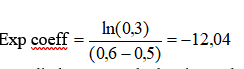Difference between revisions of "NVGate Time windows"
(Created page with " <font color="#7F9698"></font>Used to define time weighting windows that can be applied to FFT blocks. framed|none =====Force===== This setti...") |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
[[Image:Filter_builder_08.png|framed|none]] | [[Image:Filter_builder_08.png|framed|none]] | ||
=====Video tutorial===== | |||
<youtube>https://youtu.be/gPVnbq0-K8E</youtube> | |||
=====Force===== | =====Force===== | ||
| Line 42: | Line 46: | ||
'''Note''': it is possible to adjust the values graphically by using drag and drop on the graph. | '''Note''': it is possible to adjust the values graphically by using drag and drop on the graph. | ||
Revision as of 12:41, 18 May 2020
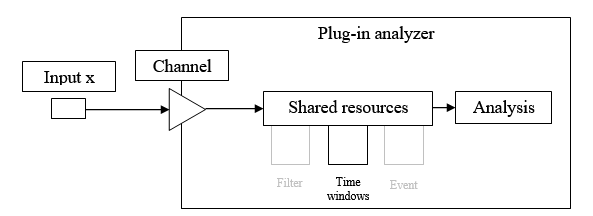
Used to define time weighting windows that can be applied to FFT blocks.
Video tutorial
Force
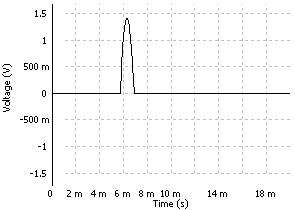
This setting is generally used to set up a uniform time window around the interesting part of the signal such as hammer impact, for example.
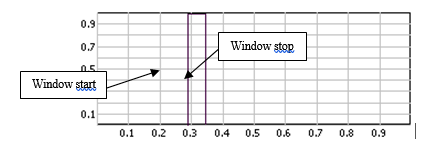
- Window Start: Starting point of the window as a percentage of the triggered block size of the plug-in using the window. The block size is the plug-in resolution setting value multiplied by 2.56. ex: for 401 lines resolution the triggered block size is 401*2.56 = 1024 samples.
- Window Stop: Stopping point of the window in percentage of the triggered block size of the plug-in using the window. The block size is the plug-in resolution setting value multiplied by 2.56. ex: for 401 lines resolution the triggered block size is 401*2.56 = 1024 samples.
Note: it is possible to adjust the start and stop values graphically by using drag and drop on the graph.
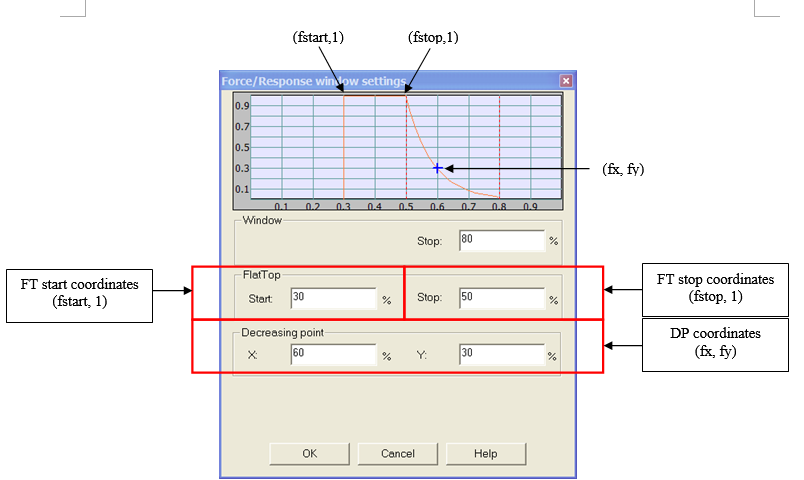
Response
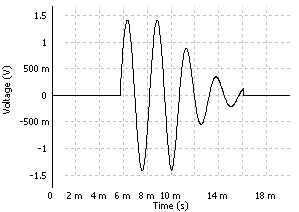
This setting is generally used to set up a uniform time window around the interesting part of the signal such as the response of an accelerometer after a hammer impact, for example.
- Window Stop: Stopping point of the window as a percentage of the triggered block size of the plug-in using the window. The block size is the plug-in resolution setting value multiplied by 2.56. ex: for 401 lines resolution the triggered block size is 401*2.56 = 1024 samples.
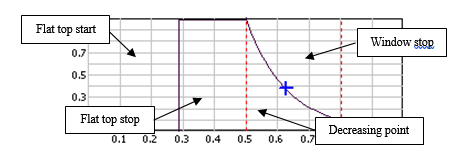
- Flat top Start: Starting point of the window flat top as percentage of the triggered block size of the plug-in using the window. The block size is the plug-in resolution setting value multiplied by 2.56. ex: for 401 lines resolution the triggered block size is 401*2.56 = 1024 samples.
- Flat top Stop: Stopping point of the window flat top as a percentage of the triggered block size of the plug-in using the window. The block size is the plug-in resolution setting value multiplied by 2.56. ex: for 401 lines resolution the triggered block size is 401*2.56 = 1024 samples.
- Decreasing point X: Abscissa of the intermediate point that determines the decreasing coefficient of the exponential function as a percentage of the triggered block size of the plug-in using the window. The block size is the plug-in resolution setting value multiplied by 2.56. ex: for 401 lines resolution the triggered block size is 401*2.56 = 1024 samples.
- Decreasing 'point Y': Ordinate of the intermediate point that determines the decreasing coefficient of the exponential function as a percentage of the value of the signal.
- Exponential coefficient: this coefficient is calculated with the coordinates of Decreasing point Y and Decreasing point X.
In this example, it then gives
Note: a time window can be applied to several plug-in analyzer channels. The modification of the time window values will be applied to all the channels the time window is active.
Note: it is possible to adjust the values graphically by using drag and drop on the graph.