Difference between revisions of "NVGate Transducer and Calibration"
(Created page with "=====Transducer group===== This group manages the transducers database which is used by NVGate to automatically setup the inputs and trace front-end status at measurement time...") |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 08:41, 20 April 2020
Transducer group
This group manages the transducers database which is used by NVGate to automatically setup the inputs and trace front-end status at measurement time.
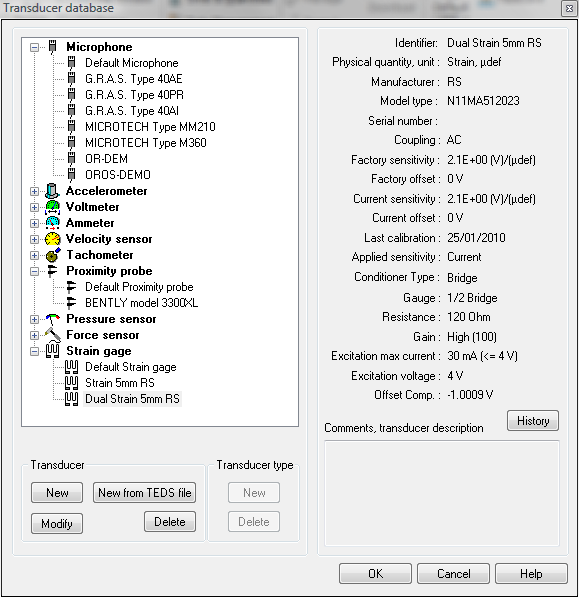
Database: Opens the transducer database dialog The left side displays all the transducers in the database in a tree form. They are grouped by type. For each type of transducer, there is a default transducer. The right side displays the information about the selected transducer.
- New: This button is available when a transducer or a transducer type is selected. It is called the "new transducer" dialog box. If a transducer is selected, all information related to the transducer is applied to the new transducer.
- New from TEDS file: This button allows opening a file .ted and so creating a new transducer with its characteristics in the transducers database.
- Delete: This button is not available when a default transducer is selected. It removes the selected transducer from the database.
- Modify: This button is not available when a default transducer is selected. It is used to modify the characteristics of the transducer. Clicking on the modify or new button opens the transducer definition dialog box:
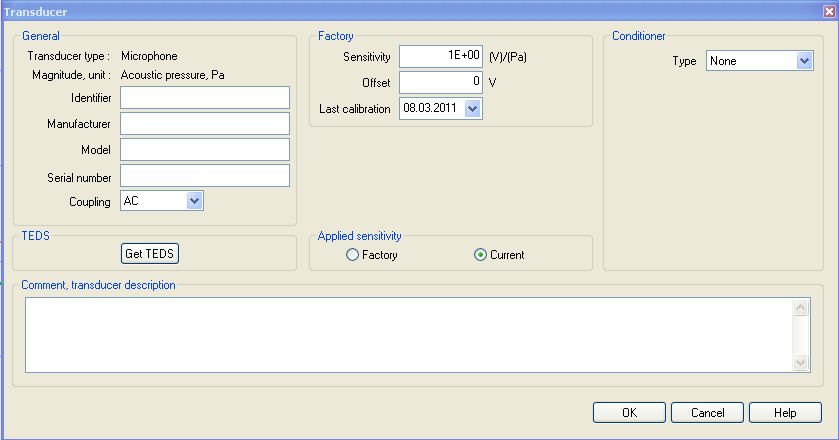
- Transducer type: Can be a pre-defined type (microphone, accelerometer...) or a user-defined type.
- General:
Magnitude, unit: Magnitude and unit associated with the transducer type
Identifier: Name that will be used to identify the transducer. This identifier must be unique. This is the only field that must be filled in. The others contain optional information.
Manufacturer: Name of the company that manufactures the transducer.
Model: Identifies the transducer.
Serial number: Unique identification, this must appear on the transducer itself.
Coupling: When the transducer is connected to an input, this coupling will automatically be set.
- TEDS:
By clicking on Get TEDS, a file .ted can be selected to set automatically the characteristic values of the transducer.
- Factory values: Sensitivity, offset, last calibration.
These values can usually be found on the calibration chart of the transducer. For maintenance calibration, use the update button to set the new values
- Current values: Sensitivity, offset, last calibration.
Displays the current sensitivity and offset. The update button may be used to set new values, in the event the transducer is not calibrated with NVGate.
The history button is used to retrieve all calibrations that have been performed on the transducer.
- Applied sensitivity:
Factory: applies sensitivity of the calibration chart of the transducer.
Current: applies sensitivity read on the TEDS file of the transducer.
- Comment, transducer description: Free text area
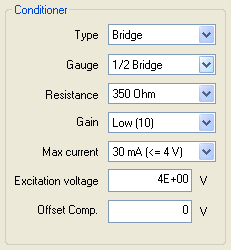
- Conditioner: Has to be change if you use and X-Pod conditioner. The XPod is a device that can be fixed on the OR362/OR382 side.
- Type: bridge signal conditioning for strain gauges, dynamic pressure, force and acceleration measurements.
- Gauge type: Full, Half or Quarter bridge mount. The completion resistors are included in the Xpod,
- Resistance: Bridge completion resistor: 120 or 350 Ohms for quarter bridge mount.
- Gain: Bridge gain: 10 or 100 depending on the required precision and range.
- Max current: the provided current can be limited to 30 mA up to 4 V and 12 mA up to 10 V.
- Excitation voltage: Each Xpod provides an excitation voltage from 0 to 10 V.
- Offset Comp.: Bridge offset comp: Can be used for manual balance of the bridge,
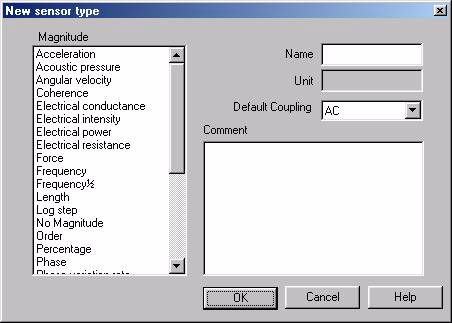
- New Transducer Type: This button is available when a transducer type is selected. A new transducer type is necessary when the pre-defined type does not fit the needs. It is used to gather transducers with the same magnitude.
- Magnitude: Magnitude that will be associated with the transducer type and all transducers of this type.
- Name: This name will be used to identify the type. It must be unique.
- Unit: Current unit of the magnitude.
- Default coupling: default coupling value that will be used when a new transducer is created. This value can be changed individually.
- Comment: Free text area
History: This tool is used to see how transducer sensitivity and offset change over time. Information about every calibration is displayed, making it easy for the user to see if the transducer behavior is constant.
- Current sensitivity: This is the sensitivity level obtained during the last calibration. If the transducer has never been calibrated, the factory sensitivity is selected. This sensitivity is used when the transducer is selected on an input
- Current offset: This is the offset obtained during the last calibration. If the transducer has never been calibrated, the offset sensitivity is selected. This offset is used when the transducer is selected on an input
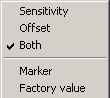
- Graph: Displays the calibration values. A pop-up menu is available by right clicking on the graph.
It is used to select the sensitivity graph, the offset graph or both. It is also possible to hide/display the factory values. There is also a marker to highlight the calibration.
Merge multiple transducer databases into one. The merged TDB is the one currently used by NVGate (file: transducers.tdb located in the NVGate.exe directory) Clicking on Merge open the database to merge browser. Both native (.cdb) and comma separated values (.txt) formats are available. For the csv, the format is the same as the export one, with one line per transducer.
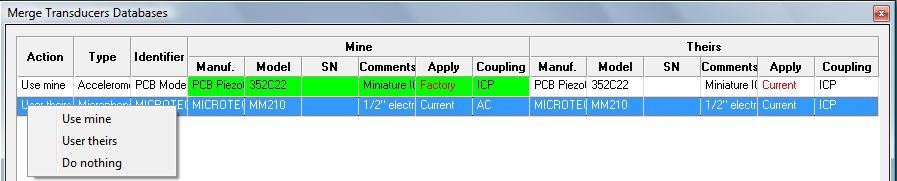
In case of conflict (the same transducer does not features the same setup in the 2 databases) a specific dialog box is proposed.
Only conflict lines are displayed.
- On the left side the current NVGate® database called Mine
- On the right side the imported one called Theirs
The non-matching settings are written in red, and the current choice (the one which will be saved) is shown on a green background. The default choice is to save the current NVGate® settings (Mine).
The operator may apply 3 types of operations, selected by a right click on the line of interest:
- Use mine: The current NVGate® setting is kept. The calibration histories from the imported and current database are merged.
- Use theirs: The imported setting will be applied and saved. The calibration histories from the imported and current database are merged.
- Do nothing: The corresponding transducer is ignored and nothing is changed
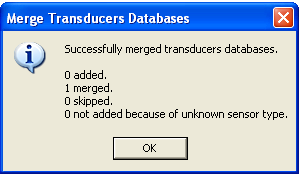
At the end of the merge operation a summary of the modification is presented
Export: Allows exporting the current database (file: transducers.tdb located in the NVGate.exe directory) in csv format.
The exported file contains one line per transducer with the following field.
Only the latest site calibration information are exported in the txt file.
Transducers group
Manage the transducers calibration and automatic recognition prior to measurements:
Calibration: Initiates the calibration procedure tool.
All current analyses and recording must be stopped prior switching to calibration.
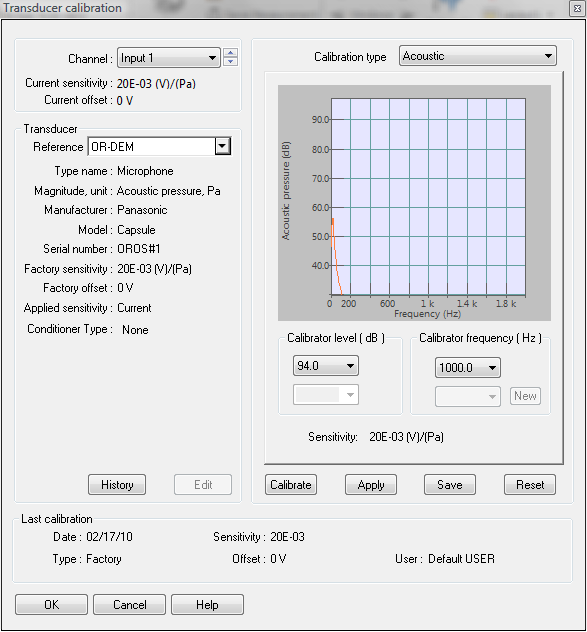
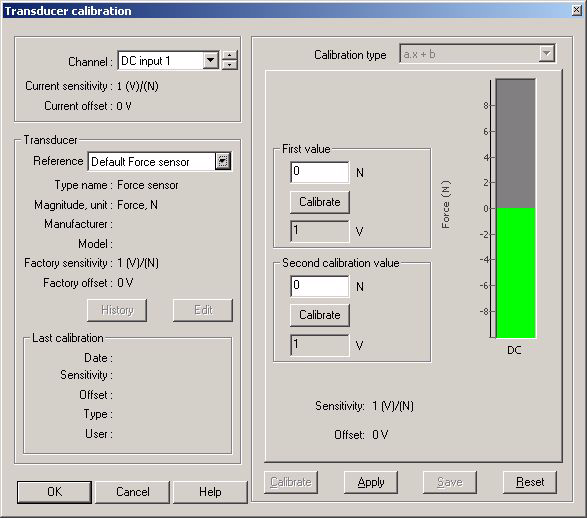
The following dialog box is used to calibrate the inputs connected to a transducer.
- Channel: This is the channel to be calibrated. It can be selected using the drop-down list or the up and down arrow. It is available for calibration of all dynamic and DC inputs. When a channel is selected, the sensitivity and the offset are immediately updated.
- Reference: This is the transducer selected on the channel. It is necessary to select a transducer in order to calibrate the input. If the transducer used is not in the list, a default transducer can be used. Information about the transducer is displayed.
- History: See "Transducer" chapter p 82. This button is not available when a default transducer is selected, since it does not refer to unique transducer.
- Edit: Similar to the "new transducer dialog".
- Calibration type: This field is automatically updated, depending on the type of transducer selected.
| Calibration type | Description |
| Acoustic | The transducer is a microphone |
| Vibration | The transducer is an accelerometer (possible unit in g or in m/s²) |
| Frequency | The transducer is associated with a dynamic input and is not a microphone or an accelerometer |
| a.x + b | The transducer is associated with a DC input
|
- Acoustic, vibration and frequency calibration: The spectrum measured is displayed. The frequency range is linked to the calibrator frequency. It is possible to right click in the plot area to perform an auto-scale on the Y-axis.
- Calibrator level: Indicates the level of the calibrator. This values is used to determine the new sensitivity of the transducer
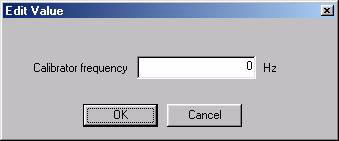
- Calibrator frequency: Indicates the frequency of the calibrator. It is used to check that the maximum level measured is at the correct frequency. It is also used to select the best frequency range for the calibration. The most common calibrator frequencies are suggested. It is also possible to choose a user-defined frequency.
- New: Used to select a user-defined calibrator frequency
- Calibrate: Starts the calibration. The analyzer detects the maximum level, checks that frequency is near the calibrator frequency, and determines the new sensitivity.
NB: In case of 1-DSP analyzer with 4 inputs @ 51,2kHz connected to the octave plug-in, it is not possible to perform the calibration (DSP power limit reached). In such situation, down the sampling frequency to 25,6kHz or disconnecting the inputs from the octave plug-in for the time of the calibration will allow calibrating the sensors.
Detect TEDS: Start the sequence for detecting transducers (or missing one) equipped with an electronic datasheet inside (TEDS: Transducer Electronic Data Sheet) connected to the front end.
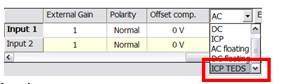
As the TEDS sequence occurs automatically when an input coupling is set to ICP+TEDS, the Detect TEDS button is used for re-checking after transducers or cables modifications. The result of check will be visible on the warning window and may lead to add new transducers to the TDB.
Only the inputs with their coupling set to ICP+TEDS will be checked.
Applying the ICP+TEDS coupling to any (set of) input(s) will activate a recognition sequence on the corresponding input(s). The result can be the following;
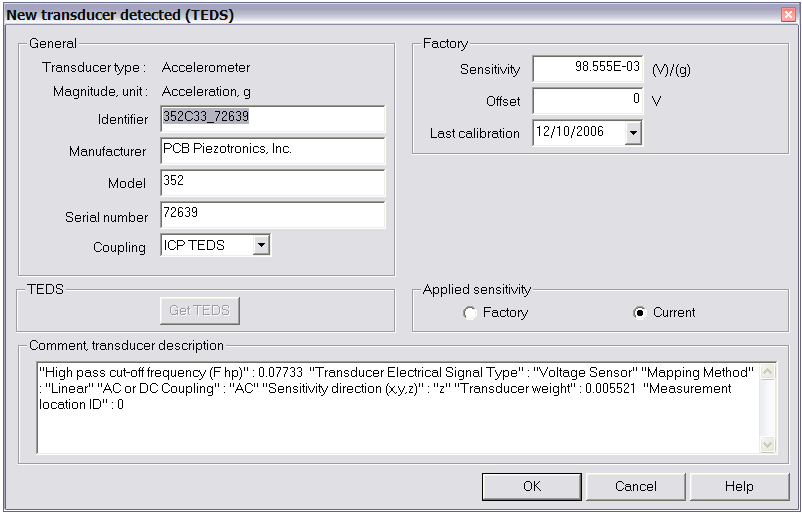
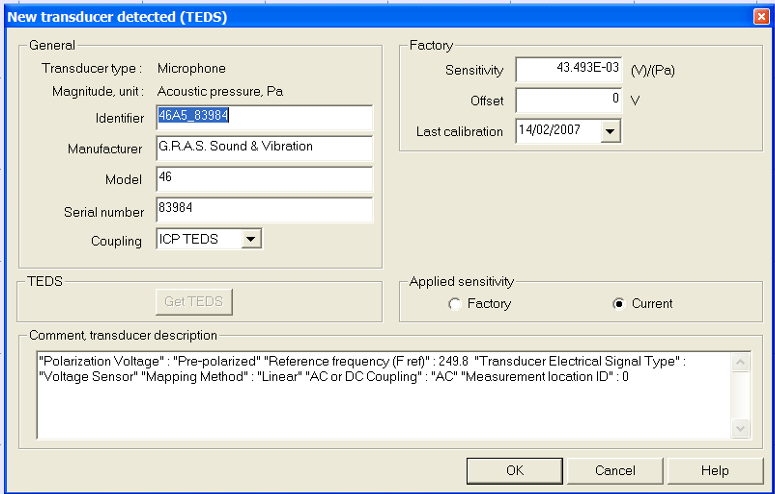
- A new transducer (not in the current NVGate® transducers database) is connected to the corresponding input. NVGate® proposes to add the new transducer in the Transducer database. A dialog box lets the user change the transducer properties:
The content of the TEDS is used to fill the transducer properties. The data from the TEDS that have no correspondence in the transducer database are copied in the comment area. The name is proposed as the concatenation of type and serial number. User may change it.
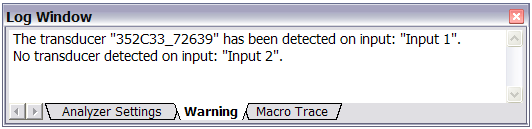
- A known transducer (existing in the database) is recognized in the corresponding input. NVGate® will notice it in the log window (which is popped up automatically).
- There is no TEDS transducer connected to the corresponding input. A warning is issued in the log window for each input in this situation.
Warning the TEDS Detection will applies a negative voltage (-5 V) to the corresponding inputs, this may affect incompatible transducers.
OROS 3-Series TEDS management fulfills the IEEE 1451.4 - 2004 revision 1 standard for:
|
Template # 25 |
|
Template # 27 |
|
Template # 28 |
|
Template # 29 |
The transducers which are compatible with IEEE 1451.4 - 2004 revision 1 are automatically recognized by the OROS 3-Series analyzers. In order to protect transducers that are electrically incompatible with the TEDS reading, there is a special coupling ICP + TEDS.
All other transducers types will generate a warning specifying that they are not supported.
There are two ways to add a TEDS transducer to the transducers data base:
Connect a TEDS transducer on a channel.
Select ICP TEDS for the input coupling.
All the characteristics of the transducer are automatically detected.
A warning confirms that a new transducer has been detected.
The window below is displayed.
The new transducer is added to the transducer database.
- Used a TEDS File
To use a TEDS file, click on New from TEDS file in the transducer database window.
By selecting the file, all the characteristics of the transducer are imported in the transducer database where anew transducer is added.